What Two Substances Are Given Off During Respiration and Used Again During Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemic energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide.

Photosynthesis definition states that the process exclusively takes identify in the chloroplasts through photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene and xanthophyll. All green plants and a few other autotrophic organisms utilize photosynthesis to synthesize nutrients past using carbon dioxide, h2o and sunlight. The past-product of the photosynthesis process is oxygen.Let the states have a detailed look at the process, reaction and importance of photosynthesis.
What Is Photosynthesis in Biology?
The discussion "photosynthesis" is derived from the Greek words phōs (pronounced: "fos") and σύνθεσις (pronounced: "synthesis") Phōs means "light" and σύνθεσιςmeans, "combining together." This means "combining together with the help of lite."
Photosynthesis also applies to other organisms likewise green plants. These include several prokaryotes such every bit cyanobacteria, purple leaner and green sulfur bacteria. These organisms exhibit photosynthesis only like green plants.The glucose produced during photosynthesis is then used to fuel various cellular activities. The by-product of this physio-chemical process is oxygen.
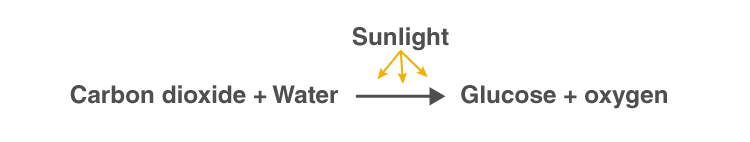
A visual representation of the photosynthesis reaction
- Photosynthesis is also used past algae to catechumen solar free energy into chemical energy. Oxygen is liberated every bit a by-product and lite is considered as a major factor to complete the process of photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis occurs when plants use low-cal energy to catechumen carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Leaves comprise microscopic cellular organelles known every bit chloroplasts.
- Each chloroplast contains a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules whereas carbon dioxide and oxygen enter through the tiny pores of stomata located in the epidermis of leaves.
- Another past-production of photosynthesis is sugars such as glucose and fructose.
- These sugars are then sent to the roots, stems, leaves, fruits, flowers and seeds. In other words, these sugars are used by the plants equally an free energy source, which helps them to grow. These sugar molecules then combine with each other to class more circuitous carbohydrates like cellulose and starch. The cellulose is considered as the structural material that is used in constitute cell walls.
Where Does This Procedure Occur?
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis in plants and bluish-dark-green algae. All green parts of a plant, including the green stems, green leaves, and sepals – floral parts comprise of chloroplasts – green colour plastids. These cell organelles are nowadays only in found cells and are located within the mesophyll cells of leaves.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis procedure requires several factors such as:
- Light Intensity: Increased light intensity results in a higher rate of photosynthesis. On the other mitt, low light intensity results in a lower rate of photosynthesis.
- The concentration of CO2: College concentration of carbon dioxide helps in increasing the rate of photosynthesis. Ordinarily, carbon dioxide in the range of 300 – 400 PPM is adequate for photosynthesis.
- Temperature: For efficient execution of photosynthesis, it is important to have a temperature range between 25° to 35° C.
- H2o: As water is an of import gene in photosynthesis, its deficiency can atomic number 82 to problems in the intake of carbon dioxide. The scarcity of water leads to the refusal of stomatal opening to retain the corporeality of water they have stored inside.
- Pollution: Industrial pollutants and other particulates may settle on the leaf surface. This can block the pores of stomata which makes it difficult to take in carbon dioxide.
Also Read:Photosynthesis Early Experiments
Photosynthesis Equation
Photosynthesis reaction involves 2 reactants, carbon dioxide and water. These two reactants yield 2 products, namely, oxygen and glucose. Hence, the photosynthesis reaction is considered to exist an endothermic reaction. Following is the photosynthesis formula:
6CO2 + 6H2O —> Chalf-dozenH12Ovi + 6Oii
Unlike plants, certain bacteria that perform photosynthesis exercise not produce oxygen as the past-product of photosynthesis. Such bacteria are called anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. The leaner that do produce oxygen as a past-production of photosynthesis are called oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria.
Photosynthetic Pigments
At that place are four different types of pigments present in leaves:
- Chlorophyll a
- Chlorophyll b
- Xanthophylls
- Carotenoids
Structure Of Chlorophyll
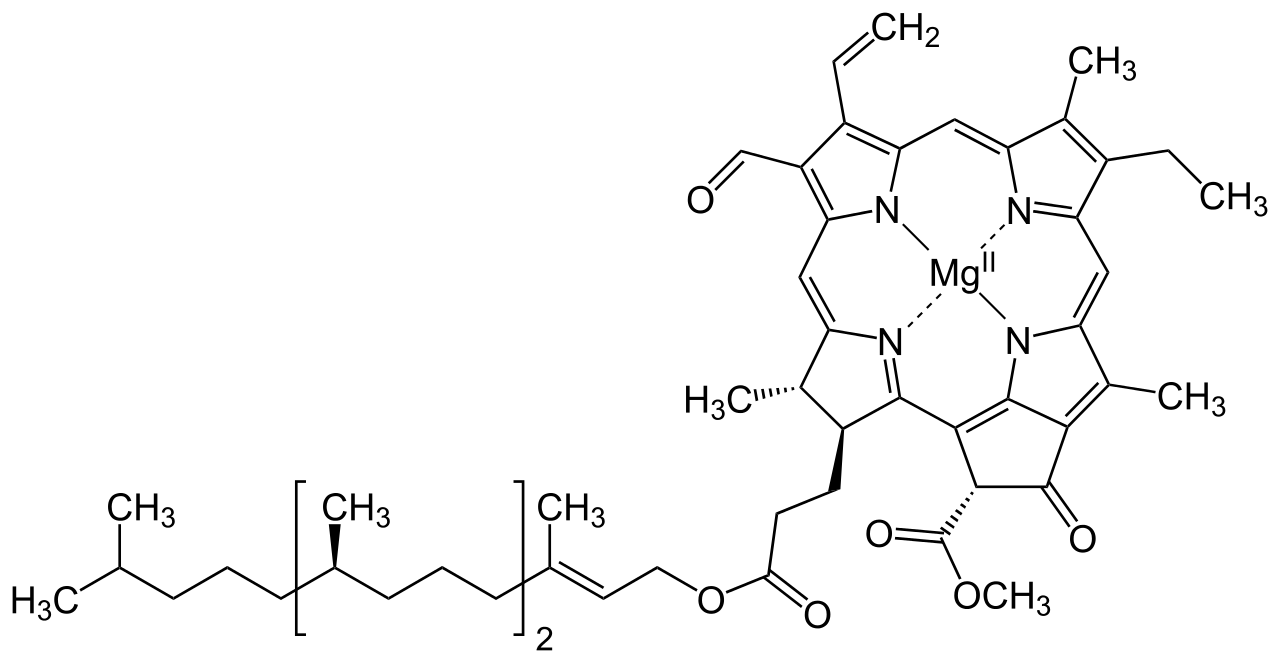
The structure of Chlorophyll consists of 4 nitrogen atoms that surround a magnesium atom. A hydrocarbon tail is likewise present. Pictured higher up is chlorophyll-f,which is more effective in nigh-infrared calorie-free than chlorophyll-a
Chlorophyll is a dark-green paint constitute in the chloroplasts of thefound celland in the mesosomes of blue-green alga. This green colour pigment plays a vital role in the procedure of photosynthesis by permitting plants to absorb energy from sunlight. Chlorophyll is a mixture of chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b.Besides greenish plants, other organisms that perform photosynthesis contain various other forms of chlorophyll such as chlorophyll-c1, chlorophyll-c2, chlorophyll-d and chlorophyll-f.
As well Read: Biological Pigments
Procedure Of Photosynthesis
At the cellular level, the photosynthesis process takes place in prison cell organelles chosen chloroplasts. These organelles contain a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll, which is responsible for the characteristic green colouration of the leaves.
Every bit already stated, photosynthesis occurs in the leaves and the specialized cell organelles responsible for this procedure is called the chloroplast. Structurally, a leaf comprises a petiole, epidermis and a lamina. The lamina is used for absorption of sunlight and carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
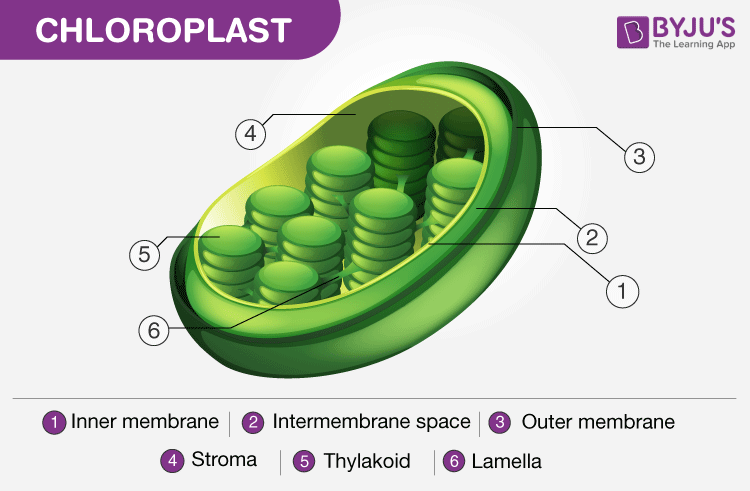
Construction of Chloroplast. Annotation the presence of the thylakoid
"Photosynthesis Steps:"
- During the procedure of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters through the stomata, h2o is absorbed by the root hairs from the soil and is carried to the leaves through the xylem vessels. Chlorophyll absorbs the calorie-free energy from the dominicus to split h2o molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The hydrogen from water molecules and carbon dioxide absorbed from the air are used in the production of glucose. Furthermore, oxygen is liberated out into the atmosphere through the leaves equally a waste product production.
- Glucose is a source of food for plants that provide energy forgrowth and development, while the rest is stored in the roots, leaves and fruits, for their later utilize.
- Pigments are other fundamental cellular components of photosynthesis. They are the molecules that impart colour and they absorb light at some specific wavelength and reflect back the unabsorbed light. All green plants mainly incorporate chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids which are present in the thylakoids of chloroplasts. It is primarily used to capture light energy. Chlorophyll-a is the main paint.
The process of photosynthesis occurs in ii stages:
- Light-dependent reaction or light reaction
- Light independent reaction or night reaction
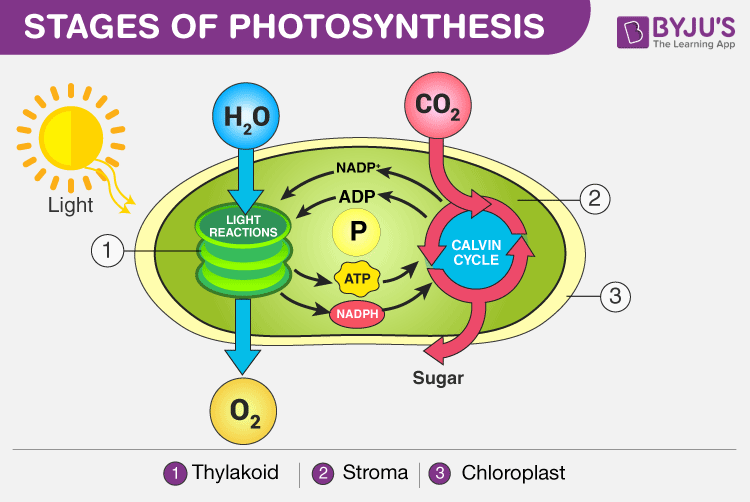
Stages of Photosynthesis in Plants depicting the two phases – Light reaction and Nighttime reaction
Calorie-free Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Low-cal-dependent Reaction
- Photosynthesis begins with the low-cal reaction which is carried out merely during the twenty-four hours in the presence of sunlight. In plants, the calorie-free-dependent reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
- The Grana, membrane-bound sacs like structures present inside the thylakoid functions by gathering light and is chosen photosystems.
- These photosystems have big complexes of pigment and proteins molecules nowadays within the plant cells, which play the primary role during the process of light reactions of photosynthesis.
- There are ii types of photosystems: photosystem I and photosystem Ii.
- Nether the light-dependent reactions, the low-cal free energy is converted to ATP and NADPH, which are used in the 2d phase of photosynthesis.
- During the calorie-free reactions, ATP and NADPH are generated by 2 electron-transport chains, water is used and oxygen is produced.
The chemical equation in the calorie-free reaction of photosynthesis can be reduced to:
2H2O + 2NADP+ + 3ADP + 3Pi → O2 + 2NADPH + 3ATP
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Low-cal-independent Reaction
- Night reaction is also called carbon-fixing reaction.
- It is a light-independent procedure in which sugar molecules are formed from the water and carbon dioxide molecules.
- The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast where they utilize the NADPH and ATP products of the light reaction.
- Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and go on to the Calvin photosynthesis cycle.
- In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH formed during light reaction drive the reaction and convert 6 molecules of carbon dioxide into one saccharide molecule or glucose.
The chemical equation for the dark reaction can be reduced to:
3CO2 + half-dozen NADPH + 5H2O + 9ATP → G3P + 2H+ + 6 NADP+ + 9 ADP + 8 Pi
* G3P – glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
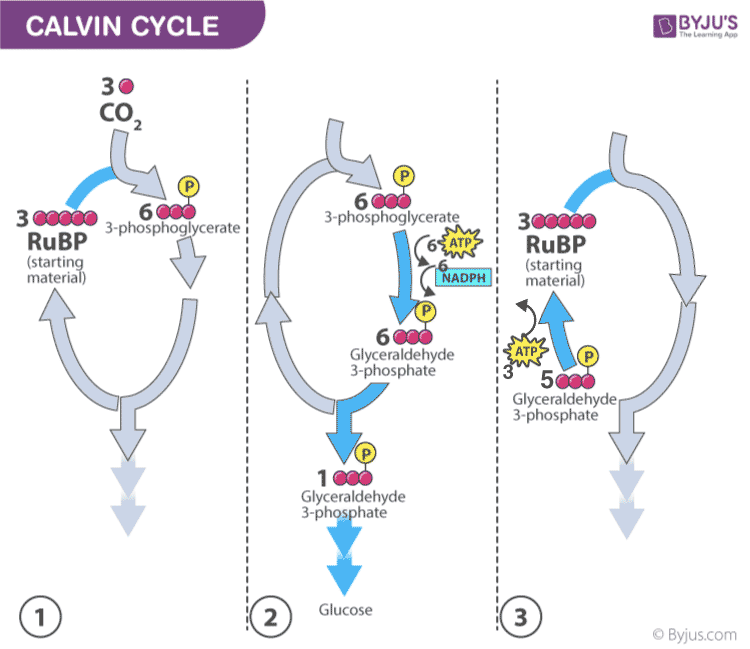
Calvin photosynthesis Cycle (Dark Reaction)
Besides Read:Cyclic And Not-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Importance of Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is essential for the existence of all life on world. Information technology serves a crucial role in the food chain – the plants create their food using this process, thereby, forming the primary producers.
- Photosynthesis is also responsible for the production of oxygen – which is needed past about organisms for their survival.
Frequently Asked Questions
ane. What is Photosynthesis? Explain the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is a biological process utilized past all greenish plants to synthesize their own nutrients. The process of photosynthesis requires solar energy, h2o and carbon dioxide. The by-product of this process is oxygen.
2. What is the significance of Photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, oxygen gas is liberated out into the environment and is utilized past humans, animals and other living species during the process of respiration.
3. List out the factors influencing Photosynthesis.
There are several factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis. Lite intensity, water, soil pH, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature and other climatic conditions are the main factors affecting the charge per unit of photosynthesis.
4. What are the different stages of Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis takes place in two stages, namely lite-dependent reactions and calorie-free-independent reactions. Calorie-free-dependent reactions are also called lite reactions and occur during the 24-hour interval fourth dimension. Light-independent reaction is also called the dark reaction or the Calvin bicycle.
5. What is the Calvin Cycle?
The Calvin cycle is also chosen the calorie-free-independent reaction. The complete process of the Calvin wheel takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
half-dozen. Write down the Photosynthesis Equation.
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/photosynthesis/
Post a Comment for "What Two Substances Are Given Off During Respiration and Used Again During Photosynthesis"